Examples of Sample Labels
| Site M | Yr 01 | S'vsr JVF |
| Field A | Sq. 13 | Locus 17 |
| Pail 3 | Date (dy/mth/yr) | |
| Info. | 10/07/01 | |
| floor | ||
| Site | THY 01 | |
| Context | 15 | |
| Sample No. | 3 | |
| Info. | hearth | |
The outside labels are prone to fall off, or be eaten by inquisitive sheep or rats, so putting an extra label in the bags, often prevents the sample becoming void.
Equipment Needed for Flotation
- water tank with spout
- 2 settling tanks
- pump and tubing
- 1m² mesh with 1mm holes
- 1mm sieve
- 300 mµ sieve
- tea strainer
- bulldog clips
- re-enforced paper and string
How does flotation work?
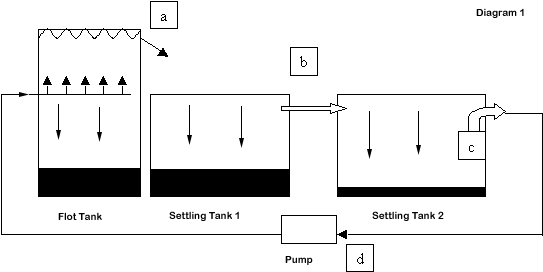
The basic idea behind flotation is that charred material floats. A large water filled tank acts as the receptacle. If water is at a premium, it can be recycled by connecting two settling tanks. The water from the flot tank runs into the first settling tank (a). The majority of the mud settles here. The water then drains into the second tank (b), where most of the remaining mud falls out. A filter (c) is placed on the end of the last pipe to reduce contamination, thereby pumping relatively clean water back around to the flot tank (d).